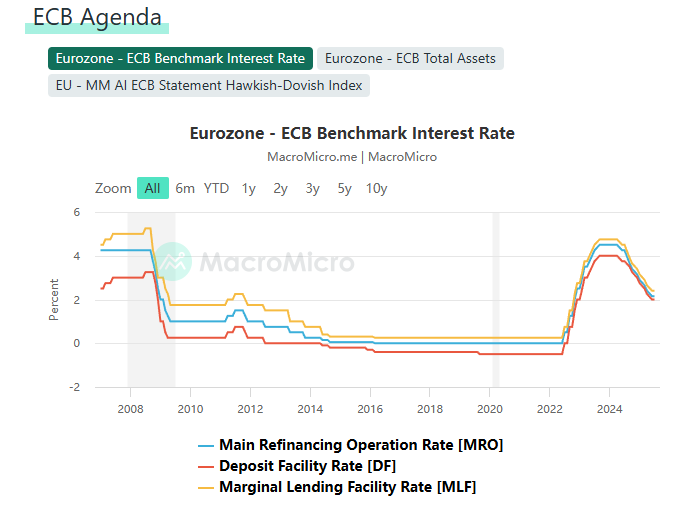
Since the dawn of the 21st century, major global economies have maintained prolonged periods of low interest rates to stimulate economic growth, establishing a stable low-interest-rate macroenvironment. However, in recent years, driven by factors such as elevated inflation and tightening monetary policies, the global interest rate landscape has embarked upon a structural transition from prolonged low rates towards higher rates. This shift has profoundly impacted the pricing logic of financial markets and investors' asset allocation frameworks. Traditional allocation strategies now face the risk of becoming obsolete, creating an urgent need for systematic research to provide theoretical and practical support. Focusing on the impact of evolving interest rate environments on investors' asset allocation decisions, this analysis examines asset performance across different interest rate cycles, with a specific emphasis on transition periods. By examining representative cases of high and low interest rates, it traces the historical performance of various asset classes during distinct interest rate phases and presents data analysis. Research findings indicate that bonds and growth equities demonstrate superior performance during low-interest-rate periods, while value equities, commodities, and cash-like assets yield more stable returns during high-interest-rate phases. Key signals identifying interest rate transition periods—such as unexpected inflation surges and central bank policy shifts—are identified. Risk management strategies proposed include diversified allocation, dynamic duration adjustment, and increased allocation to inflation-hedging assets, offering practical guidance for investors to navigate interest rate cycles and optimise asset allocation.