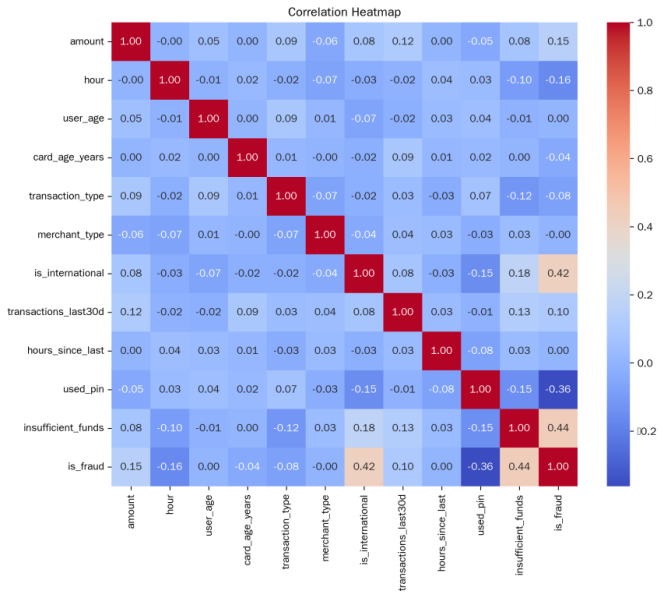
With China’s overall victory in the battle against poverty, consolidation and expansion of poverty alleviation results and preventing a large-scale relapse into poverty have become key problems of the new era. Rural households suffer especially significant poverty vulnerability issues as a result of their sole source of income and weak risk resistance abilities. How digital inclusive finance influences the vulnerability of rural households to poverty and what its mechanisms are need thorough theoretical research and empirical testing. Based on China Household Finance Survey data and Digital Inclusive Finance Index, this study examines the impact effects and mechanisms of digital inclusive finance on the poverty vulnerability of rural households by Probit model. It creates a set of overall indicators for the poverty vulnerability of rural households including financial margins, debt servicing capability, and risk insurance capacity, and divides it into four levels. From the empirical results, it can be seen that digital inclusive finance has played a positive role in poverty reduction risks of rural household, and it shows a strong anti-poverty effect. From the mechanism test results, it can be seen that financial asset diversification is a channel through which digital inclusive finance affects the rural poverty vulnerability, because digital inclusive finance helps the rural households to allocate their financial assets in a more diversified way, thus reducing their poverty vulnerability. The research conclusions can provide significant theoretical foundation and policy reference for consolidating and expanding the results of poverty alleviation, as well as preventing a large-scale return to poverty.