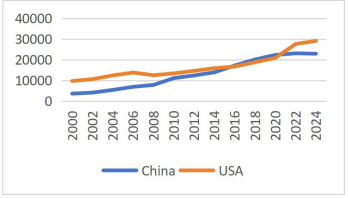
Since 2000, housing prices in China have risen steeply, maintaining high levels similar to those in the US despite China's lower GDP per capita, increasing local residents’ pressure and challenging the stability of the Chinese financial market. The core issue lies in China's land policy. In China, urban land is owned by the government, and developers must pay land transfer fees to gain usage rights. These fees constitute 30%-50% of housing prices and are a major source of local government revenue, covering about 50% of their income. High land transfer fees are closely linked to local governments' financial needs and the pursuit of land-based fiscal revenue. The high housing prices caused by this have led to serious impacts such as local governments' excessive reliance on land transfer fees, increased debt risks, and low birth rates. This paper explores the causes of China's high housing prices and the issues arising from high land transfer fees and discusses the feasibility of various solutions, like fiscal substitution, to alleviate the current situation.