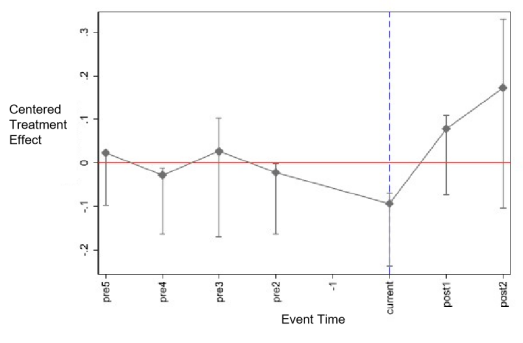
Taking the entry into force of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) in 2022 as a quasi-natural experiment, this paper systematically analyzes the impact and mechanisms of RCEP on China’s exports of high-tech products, based on panel data from 2011 to 2023 and employing the difference-in-differences (DID) method. The empirical results indicate that the implementation of RCEP has significantly boosted China’s exports of high-tech products to RCEP member countries, and this finding remains robust after a series of robustness checks. Furthermore, a mechanism analysis using the International Property Rights Index (IPRI) reveals that RCEP has significantly promoted the growth of China’s high-tech exports by enhancing the level of property rights protection. Heterogeneity analysis shows that industries such as life sciences and computer-integrated manufacturing have benefited significantly, while sectors like optoelectronics, aerospace, and telecommunications have been less affected. In addition, ICT-related exports demonstrate a notable synergistic driving effect on the overall high-tech industry exports. Based on the findings, it is recommended to provide targeted support for high-tech sectors that benefit the most, while also optimizing policies to address weaknesses in underperforming areas. Efforts should be strengthened in promoting ICT-integrated innovation and improving property rights protection to comprehensively enhance the international competitiveness of China’s high-tech industries.